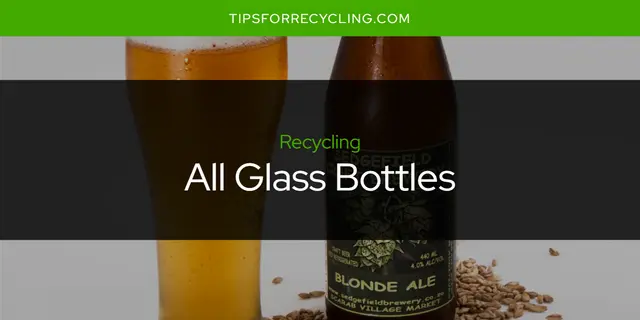
Glass recycling is the process of breaking down glass products into small pieces and reforming them into new materials for use. This method of reusing glass can have multiple benefits for both the environment and energy consumption.
Benefits
- Reduces Landfill Space - When glass is recycled, it gets diverted from landfills and other types of waste disposal systems which helps to reduce landfill space.
- Decreases Energy Consumption - Recycling glass requires very little energy during its process. The production of new glass bottles or jars from raw materials requires much more energy than their recycled counterparts, leading to a decrease in overall energy usage when recycled properly.
- Helps the Environment - As mentioned before, recycling reduces the amount that goes to landfills and creates less pollution in general as well as conserves resources within the planet’s environment by reducing extraction of raw materials from nature.
Types of Glass Recycling
There are three main types of glass recycling: clear, green, and amber.
These types can be see in various glass products such as olive oil bottles, glass cups, yankee candle jars, ceramic mugs, ceramic plates, glass beer bottles, glass candle jars, soda bottles, quaker oats containers, all glass bottles, ceramic cups, champagne bottles, christmas ornaments, coke bottles, curology bottles, glass containers, glass liquor bottles, medela bottles, mugs, and bottles.
Overview of the Three Types
Clear glass, also called transparent or flint has a very high clarity level which makes it ideal for re-use in products such as bottles, jars and windows. Green glass, sometimes referred to as light green or emerald glass, is made with iron oxide pigments that give it its color and can be used in food and beverage containers as welll as aircraft windscreens. Lastly, amber glass is produced using manganese dioxide which gives it its characteristic brownish hue that’s commonly used for beer and wine bottles.
Collection Methods Used for Each Type
Collecting each type of recyclable glass separately is essential to ensure that the highest quality materials are recovered and reused. Clear glass can typically be placed in most curbside bins without issue; however, some communities may require a specific color-coded bin for all types of colored glass. Some programs even provide specialized bins and collection points specifically for amber colored glass only.
Different Types of Sorting Techniques Used for Each Type
Sorting techniques vary depending on where the material is being processed and what type of technology is available at each facility. Manual sorting involves workers visually identifying the different colors by eye before removing them from the line by hand. Automated sorting involves the use of robotic arms or conveyor belts to separate out different colors based on their physical characteristics such as size, shape or weight.
Glass Crushing And Cullet Production
Glass crushing is the process of breaking down large pieces into smaller ones while cullet production refers to pre-processing recycled materials into small uniform particles that can then be melted down into new items such as bottles or windows. Crushing can either take place manually (by hand) or mechanically (with machines). Cullet production requires more processing steps which includes conditioning (adding water), grinding (breaking down larger pieces into smaller ones), sieving (separating out different sizes) and de-dusting (removing any dust particles).
Glass Recycling Process
Recycling glass is an important step in reducing waste and conserving resources. It is a process that takes dedication and precision to ensure that the recycled glass is pure enough to be reused. This article will discuss the collection, sorting, cleaning and processing of recycled glass, as well as the technologies used to purify it for reuse.
Collection
Collection methods used to collect recycled glass include curbside collection systems, drop-off centers, buy-back centers, and shelter programs. Each of these requires organizations or companies to actively participate in collecting the recycling materials.
Sorting, Cleaning & Processing
The first step in the sorting, cleaning and processing of recycled glass involves the removal of any contaminants from the material. This includes anything that does not belong in the recycling bin such as paper labels or plastic caps on bottles. After this has been removed, pieces are separated into different colors and sizes.
Technologies Used
To purify recycled glass for reuse two main technologies are used: the melting method and optical scanning technology. The melting method uses either a furnace or kiln to melt the material at high temperatures until it becomes liquid form again. This process removes all impurities from it (such as dirt) while also reshaping it into its original form.
Optical scanning technology is also employed during this stage of purification to separate out contaminants that may still remain at this point. Automated machinery can also be used to clean and sort materials into categories to ensure they are ready for reuse after being melted down by the furnace or kiln mentioned previously.
Through using these technologies combined with manual labor and collection techniques, recycling glass becomes an achievable endeavor with measurable results in terms of reduced waste and conservation of resources!
Reusing Recycled Glass
Glass is 100% recyclable and can be recycled an infinite number of times. Recycled glass can be used to make a variety of products such as bottles, jars, flatware, tiles, and more. Reusing recycled glass has significant benefits for the environment.
Reduction in Air Pollution
Using recycled glass instead of creating new products from raw materials reduces air pollution created by manufacturing. This decreases the amount of greenhouse gases released into the atmosphere, helping to reduce global warming.
Reduced Water Pollution
Reusing recycled glass also helps to reduce water pollution due to lower water use during manufacturing. The process requires significantly less water compared to when creating new products from raw materials, which saves both resources and energy.
Lowering Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Recycling glass also reduces energy use associated with creating new materials from scratch. This helps to lower the production of greenhouse gas emissions and contributes to preserving natural resources.
Overall, reusing recycled glass is a great way to help protect the environment while ensuring that valuable resources are not wasted in the production process.